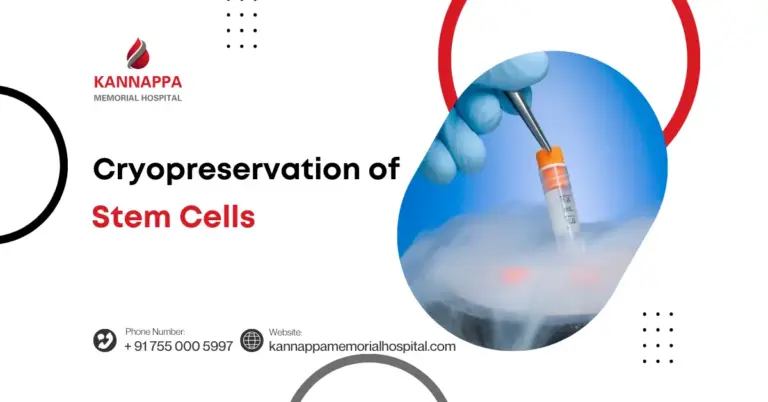
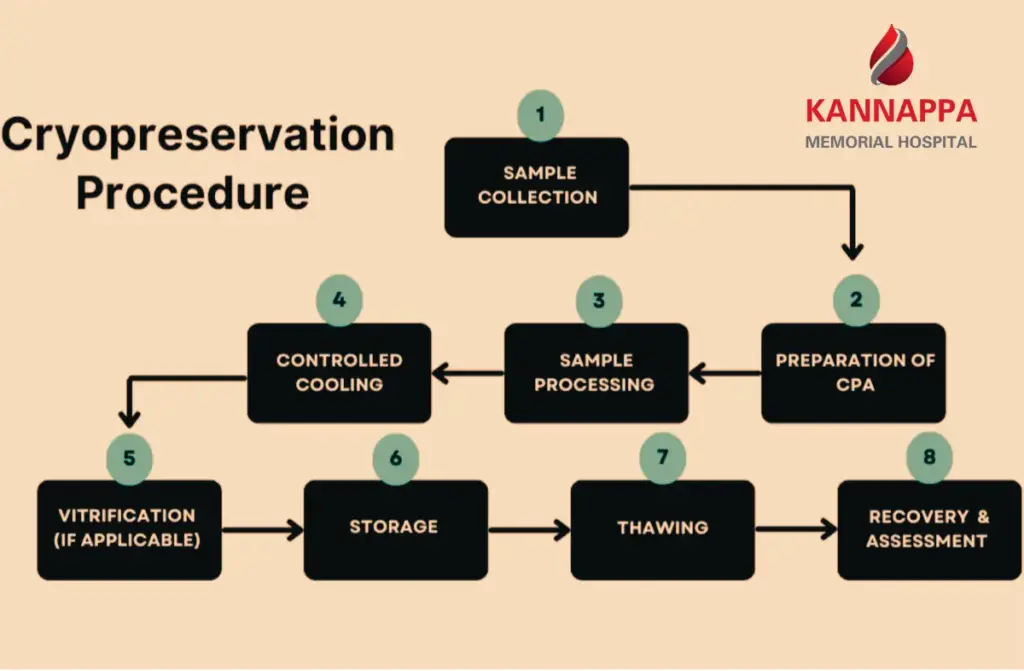
Cryopreservation is a revolutionary process that allows cells, tissues, and even organs to be preserved at ultra-low temperatures, essentially pausing their biological clock. Among its most promising applications is the cryopreservation of stem cells, which safeguards these powerful cells for future medical use. Stem cells, known for their regenerative potential, can be stored safely and later used in treatments for blood disorders, cancers, or other critical conditions. This technology also offers expectant parents an opportunity to preserve umbilical cord stem cells, securing a potential medical resource for their child’s future. For researchers, cryopreservation provides a reliable way to maintain viable stem cells for experimental therapies and clinical studies.
Cryopreservation Basics
Cryopreservation is the cornerstone of modern regenerative medicine, enabling cells to survive for extended periods under controlled freezing conditions. The process involves cooling cells to extremely low temperatures, often using liquid nitrogen, to halt all biological activity without causing damage. This technique is particularly vital for stem cells, which are highly sensitive and need precise conditions to retain their functionality for future therapeutic use.
- Principles of Cryopreservation: Cryopreservation of stem cells relies on the careful balance of temperature reduction and cryoprotective agents to prevent ice crystal formation, which can rupture cell membranes. By gradually lowering the temperature, cells enter a suspended state, maintaining viability for long-term storage.
- Role of Liquid Nitrogen: Cryopreservation in liquid nitrogen allows cells to be preserved at temperatures around -196°C. This ultra-cold environment ensures minimal metabolic activity and prevents degradation, making it ideal for storing delicate stem cells for years without loss of function.
- Cryoprotective Agents: Chemicals like dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) are commonly used to protect stem cells during freezing. These agents penetrate the cells and reduce ice formation, ensuring that cell structure and viability are preserved during both freezing and thawing.
- Applications in Medicine and Research: Cryopreserved stem cells serve multiple purposes, from supporting patients undergoing chemotherapy to enabling long-term studies in regenerative medicine. Researchers can access these preserved cells for experiments, clinical trials, and innovative therapies, ensuring consistent quality over time.
- Challenges and Considerations: Successful cryopreservation requires strict control of cooling rates, storage conditions, and thawing procedures. Any deviation can compromise cell viability, emphasizing the importance of standardized protocols and skilled laboratory practices.
Cryopreservation for Long-term Storage in Cell-based Therapies
Long-term storage of stem cells is essential for advanced medical treatments and regenerative therapies. Cryopreservation ensures that these cells maintain their regenerative potential, even after years of storage, providing a reliable source for transplantation, research, or experimental therapies. Among the most commonly preserved cells are hematopoietic stem cells, which are crucial for blood and immune system regeneration.
- Preserving Regenerative Potential: Cryopreservation of stem cells safeguards their ability to differentiate into various cell types. This ensures that when cells are eventually used in therapy, they retain their full functionality, supporting effective recovery in patients with blood disorders or organ damage.
- Use of Liquid Nitrogen for Longevity: Cryopreservation in liquid nitrogen provides an ultra-low temperature environment where cellular metabolism effectively stops. This makes it possible to store stem cells for decades without compromising their integrity, offering a dependable source for long-term therapies.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Storage: Hematopoietic stem cells, responsible for generating blood cells, are commonly cryopreserved for bone marrow transplants. Proper freezing and storage protocols ensure that these cells remain viable and functional, which is critical for patients undergoing treatments like chemotherapy.
- Cell-based Therapy Readiness: By maintaining a stock of cryopreserved stem cells, hospitals and research centers can quickly provide cells for clinical applications. This immediate availability accelerates treatment timelines and supports ongoing medical research efficiently.
- Quality Control During Storage: Regular monitoring of temperature and storage conditions is crucial to prevent cell degradation. Biobanking practices include strict protocols to ensure that cells remain viable and contamination-free throughout long-term storage.
Processing and Cryopreservation of Stem Cells
Processing and cryopreservation of stem cells is a meticulous procedure that ensures cells remain viable and functional for future therapies. Proper handling before freezing is crucial to protect these sensitive cells from damage and to maximize their therapeutic potential.
- Collection and Preparation: Stem cells, whether from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, are carefully collected under sterile conditions. Cells are then processed to remove impurities, isolate the desired population, and prepare them for cryopreservation.
- Use of Cryoprotective Agents: Before freezing, cryoprotective agents like DMSO are added to prevent ice crystal formation. These agents penetrate the cells, ensuring their structural integrity and function are maintained during the freezing process.
- Controlled-rate Freezing: Cells are gradually cooled using a controlled-rate freezer, reducing thermal shock and minimizing cellular damage. This step is critical for maintaining high cell viability after thawing.
- Long-term Storage: Processed cells are stored in liquid nitrogen tanks at -196°C. This ultra-cold environment halts metabolic activity, preserving the stem cells for years, ready for transplantation or research use.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells: Special attention is given to hematopoietic stem cells due to their sensitivity and therapeutic importance. Strict protocols are followed to ensure their viability for bone marrow transplants or regenerative treatments.
The Return of HPC Products for Transplantation
The successful reinfusion of hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) relies on proper cryopreservation and handling. Returning these cells for transplantation requires careful thawing and preparation to ensure they retain their therapeutic potential.
- Thawing and Preparation: Cryopreserved stem cells are carefully thawed in a controlled environment to avoid thermal shock. Proper thawing ensures that the cells retain their viability and functionality for transplantation.
- Biobanking Practices: Biobanking and cryopreservation of stem cells maintain strict records and storage conditions. This allows easy identification and retrieval of HPC products when required for patient treatment.
- Umbilical Cord Stem Cells: Cryopreservation of umbilical cord stem cells ensures that these cells are ready for pediatric or family-based therapies. Proper storage and handling protocols maximize their regenerative potential upon reinfusion.
- Transplant Readiness: After thawing, HPC products are assessed for cell count, viability, and purity. This guarantees that patients receive high-quality stem cells capable of restoring bone marrow and immune function.
- Clinical Impact: Timely and effective reinfusion of cryopreserved stem cells supports recovery in patients with blood disorders or cancers. This process highlights the importance of precise cryopreservation and biobanking procedures.
Reinfusions of Non-Cryopreserved Products
While cryopreservation is widely used, some stem cell products may be reinfused without freezing. Handling these non-cryopreserved cells still requires careful preparation to ensure patient safety and efficacy.
- Immediate Reinfusion: Non-cryopreserved stem cells are typically reinfused shortly after collection to preserve their function. This method is often used when transplantation timing is critical or when storage resources are limited.
- Handling and Transport: Maintaining optimal temperature and sterility during transport is essential for non-cryopreserved stem cells. This ensures the cells remain viable until they reach the patient.
- Umbilical Cord Stem Cells: Some cord blood units can be processed and reinfused without freezing, particularly in immediate therapeutic contexts. These cells retain high regenerative potential due to minimal handling time.
- Viability Assessment: Before reinfusion, non-cryopreserved cells are assessed for quality, including cell count, viability, and functionality. Ensuring these parameters is vital for the success of transplantation.
- Therapeutic Applications: Non-cryopreserved products are used in clinical scenarios where rapid cell delivery is essential, supporting faster patient recovery and reducing the risk of complications.
Quality Monitoring
Maintaining quality is paramount in stem cell cryopreservation, whether for research or clinical applications. Continuous monitoring ensures cells retain their therapeutic potential throughout storage and handling.
- Viability Checks: Regular testing of cell viability ensures that cryopreserved stem cells remain functional. This includes evaluating membrane integrity, metabolic activity, and the ability to differentiate into target cell types.
- Storage Conditions Monitoring: Liquid nitrogen levels and temperature stability are continuously tracked. Any deviations could compromise cell quality, making real-time monitoring essential for long-term storage.
- Umbilical Cord Stem Cells: Cryopreservation of umbilical cord stem cells includes specialized quality checks to verify that cells maintain their regenerative potential over the years. This supports their use in pediatric therapies.
- Documentation and Traceability: Accurate record-keeping allows tracking of each sample from collection to reinfusion. This ensures compliance with medical standards and facilitates research reproducibility.
- Risk Management: Quality monitoring also identifies potential contamination or protocol deviations early, preventing compromised cells from being used in therapies.
Other Services
Stem cell cryopreservation facilities often provide additional services that enhance research capabilities and patient care. These services ensure optimal handling and preservation of stem cells for various applications.
- Stem Cell Banking Services: Facilities offer cryopreservation of stem cells for patients, families, and researchers. This includes long-term storage, retrieval, and counseling on proper preservation methods.
- Liquid Nitrogen Storage Solutions: Cryopreservation in liquid nitrogen ensures cells remain viable for decades. Advanced storage tanks and backup systems protect against temperature fluctuations and ensure continuous preservation.
- Processing of Hematopoietic Stem Cells: Specialized services include isolation, preparation, and cryopreservation of hematopoietic stem cells for therapeutic use. These protocols maximize the success rate of bone marrow and blood cell transplants.
- Research Support: Facilities often assist researchers in storing experimental or clinical trial stem cells. This guarantees access to high-quality samples for ongoing studies and innovative therapies.
- Customized Preservation Protocols: Some centers tailor cryopreservation protocols based on cell type and intended use. This personalized approach ensures optimal cell recovery and therapeutic potential.
Conclusion
Cryopreservation of stem cells has transformed medicine by offering long-term storage for regenerative therapies, research, and transplantation. From umbilical cord stem cells to hematopoietic stem cells, precise freezing and storage protocols maintain cell viability and functionality. With advanced biobanking, liquid nitrogen storage, and quality monitoring, these cells remain ready for future medical needs. Investing in stem cell preservation today secures a powerful tool for tomorrow’s treatments. Take the step to preserve these vital cells and empower future therapies.