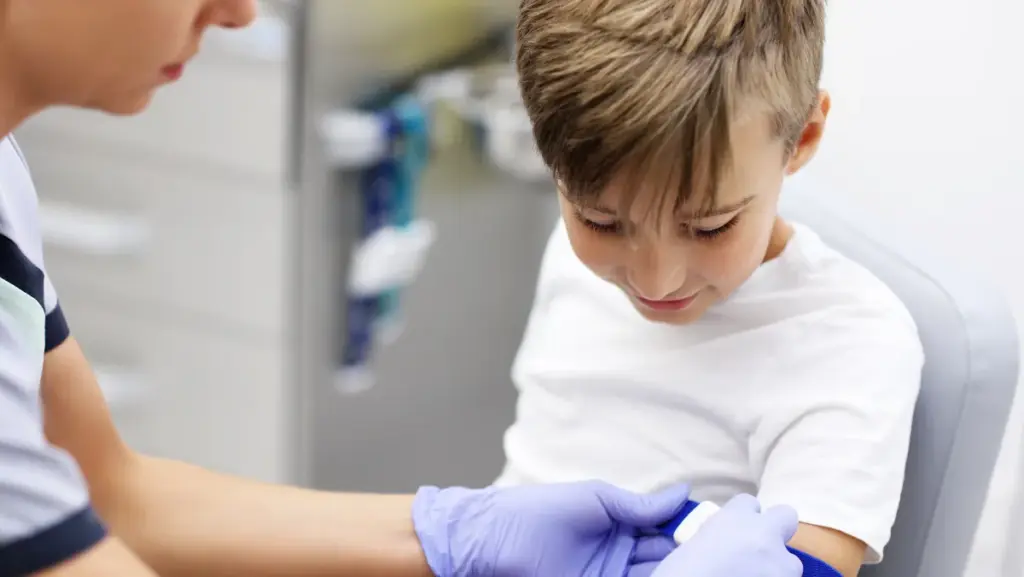
You may notice your child looks paler than usual, tires quickly during play, or doesn’t seem as energetic as before. Naturally, this can raise concern. You’re not alone—many parents face similar questions when they see these changes. In this guide, we’ll walk through what anemia is, its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and the treatments that can help children stay healthy and active.
Anemia happens when the body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to different parts of the body. Think of red blood cells as tiny delivery trucks that transport oxygen—if there aren’t enough trucks, the body’s “energy supply” runs low. This can make a child feel tired, weak, or less interested in play.
For example, a child with anemia may:
Signs of anemia can vary depending on its severity. Some children show very mild symptoms, while others may have more noticeable changes. Common signs include:
There are several reasons why a child may develop anemia:
Not all anemia is the same. Doctors usually identify the type to guide treatment.
Diagnosis usually starts with a physical exam and questions about family and diet history. Doctors often order a Complete Blood Count (CBC), which checks red cell numbers and hemoglobin levels. Additional tests may measure iron, vitamins, or screen for genetic conditions. These tests help identify the type of anemia and the best way to manage it.
Treatment depends on the type and cause of anemia:
Parents can also support their child by encouraging balanced meals, maintaining regular sleep, and following up with their pediatrician.
Hearing that your child has anemia can feel overwhelming, but remember: with today’s medical care, most children recover well and lead full, active lives. Early diagnosis, the right treatment, and ongoing support make all the difference. With guidance from your pediatrician, you can help your child grow strong, healthy, and ready to enjoy all the adventures of childhood.
You may notice your child looks paler than usual, tires quickly during play, or doesn’t seem as energetic as before. Naturally, this can raise concern. You’re not alone—many parents face similar questions when they see these changes. In this guide, we’ll walk through what anemia is, its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and the treatments that can help children stay healthy and active.
What is Anemia?
What are the Symptoms of Anemia?
What Causes Anemia?
Common Types of Anemia
How is Anemia Diagnosed?
How is Anemia Treated?
Result
Anemia happens when the body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to different parts of the body. Think of red blood cells as tiny delivery trucks that transport oxygen—if there aren’t enough trucks, the body’s “energy supply” runs low. This can make a child feel tired, weak, or less interested in play.
For example, a child with anemia may:
Signs of anemia can vary depending on its severity. Some children show very mild symptoms, while others may have more noticeable changes. Common signs include:
There are several reasons why a child may develop anemia:
Not all anemia is the same. Doctors usually identify the type to guide treatment.
Diagnosis usually starts with a physical exam and questions about family and diet history. Doctors often order a Complete Blood Count (CBC), which checks red cell numbers and hemoglobin levels. Additional tests may measure iron, vitamins, or screen for genetic conditions. These tests help identify the type of anemia and the best way to manage it.
Treatment depends on the type and cause of anemia:
Parents can also support their child by encouraging balanced meals, maintaining regular sleep, and following up with their pediatrician.
Hearing that your child has anemia can feel overwhelming, but remember: with today’s medical care, most children recover well and lead full, active lives. Early diagnosis, the right treatment, and ongoing support make all the difference. With guidance from your pediatrician, you can help your child grow strong, healthy, and ready to enjoy all the adventures of childhood.
The best treatment for anemia depends on its cause. Iron-deficiency anemia is treated with iron supplements and iron-rich foods, while vitamin-deficiency anemia may need folate or B12. More severe types, like inherited anemias, may require medications, transfusions, or special therapies. A pediatrician tailors treatment so your child regains strength safely and steadily.
Foods rich in iron, folate, and vitamin B12 support anemia recovery. Good choices include lean red meat, chicken, fish, beans, spinach, broccoli, fortified cereals, and eggs. Pairing iron-rich foods with vitamin C sources like oranges or tomatoes improves absorption. A balanced diet helps the body rebuild healthy red blood cells and restores energy.
Recovery from anemia is quicker with a combination of medical care and nutrition. Follow your doctor’s advice on supplements or medications, eat iron-rich foods daily, and include vitamin C to boost absorption. Encourage rest to restore energy. Regular blood check-ups ensure progress. With consistency, many children regain energy and strength within weeks.